The older a person gets, the higher the risk of degenerative and destructive changes, especially in the musculoskeletal system. Osteoarthritis of the ankle joint is a disease that affects the cartilage and tissue of the joints to varying degrees of severity and, if left untreated, can lead to disability. With the initial development of the pathology, the symptoms of the disease are poorly expressed, and its presence can be determined only with the help of X-rays.
What is ankle arthrosis?
The disease in which the joint cartilage and surrounding tissues are gradually destroyed is called ankle arthrosis. The basis of the pathology is a degenerative-dystrophic process, and inflammation is secondary. There is a wavy chronic course of ankle arthrosis, with variable exacerbations and remissions. The disease develops gradually. The female and male populations suffer equally from osteoarthritis. With age, the likelihood of developing pathology increases sharply.
Symptoms
Diseases of the ankle joint are exacerbated from time to time. Symptoms may not appear during remission of osteoarthritis. Pathology develops without giving itself. A person feels moderate pain in the ankle with significant physical strength, increased stiffness, and fatigue of the legs. As the pathology progresses, the pain becomes more pronounced, occurs at rest, and intensifies at night.
When the deformation of the joint is seen, the range of motion in the ankle is reduced, and a characteristic crunch and clicking sounds are heard during walking. Sometimes there is a curvature of the lower leg, the legs take the form of valgus (X-shaped) or varus (O-shaped). Initial pain is typical for ankle arthrosis, which manifests itself at the beginning of the movement after a resting state and disappears during walking.
Causes
Ankle arthrosis is divided into two groups: primary and secondary. The first arises for unknown reasons. The second develops due to negative factors: inflammation, trauma, etc. In both cases, the pathology is based on metabolic diseases of the cartilage tissue. The main reasons for the development of secondary osteoarthritis:
- damage to the ligaments due to bone deformity (fractures) or damage to the ankle;
- elongation of the joint capsule;
- compression of the nerve endings of the lumbar spine;
- excess weight;
- wear uncomfortable shoes;
- long load on the joint (intense sports, constant standing);
- diseases associated with metabolic disorders (gout, diabetes mellitus, estrogen deficiency during menopause, etc. );
- intervertebral hernia, osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine and other conditions accompanied by disorders of the lower leg, musculoskeletal system or nerve entrapment.

The degree of the disease
With ankle arthrosis, there are three degrees that are determined by device diagnostics:
- I degree - no pathological changes, there is a narrowing of the ankle joint space, compression of the talus;
- Grade II - swelling is the result of disease progression, painful sensations in the air, decreased leg mobility, joint deformity;
- Grade III - loss of amortization properties of the joint, ossification of cartilage tissue, deformity of the foot cause disability.
Possible results
Disability can be diagnosed in a patient with ankle arthrosis, because complete destruction of the joint leads to limited motor activity. To do this, the patient must undergo a medical examination. Categories of patients with disability:
- patients with progressive osteoarthritis who have been ill for more than 3 years with an outbreak of the disease at least 3 times a year;
- patients with joint surgery and life-threatening;
- patients with severe static-dynamic dysfunction.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of "second-degree osteoarthritis of the ankle joint" (or another stage) is made on the basis of a questionnaire, visual examination and laboratory results. X-rays play a crucial role. In the most advanced stages, deformed osteoarthritis and cystic formations are found in the bone area. In difficult cases, the patient is referred for a CT scan of the ankle for a more accurate assessment of bone structures. An ankle MRI may be performed to examine the soft tissues.
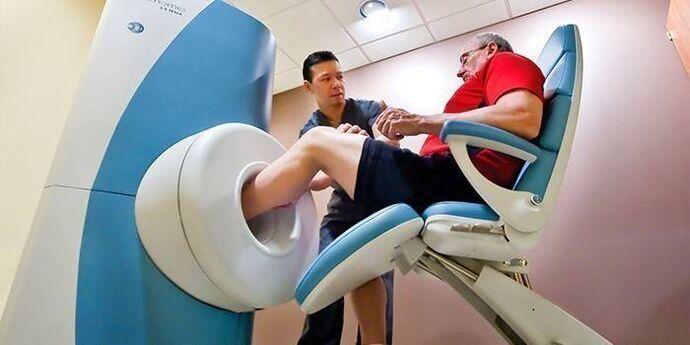
Treatment of ankle osteoarthritis
Treatment of the affected joint in post-traumatic osteoarthritis is carried out according to the general scheme. Complex treatment includes:
- elimination of pain symptoms;
- elimination of the inflammatory process;
- restoration of joint mobility;
- improvement of trophic processes;
- Restoration of normal blood circulation in the body:
- replacement of the joint with artificial prostheses (if necessary).
Medications
Drug treatment is selected taking into account the symptoms and stage of the disease. During exacerbations, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used in the form of tablets or injections. In addition, it is recommended to take local anesthetics in the form of topical or ointments. With the sensation of pain, corticosteroid medications are prescribed for intraarticular occlusions. Their application is carried out not more than 4 times a year. Drugs of the chondroprotective group are prescribed to normalize metabolism in cartilage tissue.
Ointments
Topical medications will not cure osteoarthritis or cruciate ligament of the ankle, but will speed healing and prevent recurrence. Among the effective drugs:
- A multi-component homeopathic ointment designed to treat inflammatory and dystrophic conditions of the musculoskeletal system. Apply a thin layer 1-3 times a day on the affected area. The duration of the course is 2-4 weeks. Rarely, local skin reactions occur: urticaria, burning, itching, development of dermatitis.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs with analgesic effect. Apply a small dose to the affected joints 3 times a day. The doctor determines the course of treatment individually. On average, such ointments are used until the pain disappears, but not more than 14 consecutive days.
Physiotherapy
The following physiotherapy techniques will help stop ankle arthrosis:
- Medium-wave ultraviolet radiation. Under the influence of ultraviolet waves in the affected area, there is an accumulation of substances that reduce the sensitivity of the nerve endings, which allows you to quickly eliminate the pain syndrome.
- Infrared laser therapy. The laser reduces the sensitivity of nerve roots, improves blood circulation. The procedure relieves the patient of stress caused by persistent pain in the ankle.
Diet
A special diet is indicated for inflammatory diseases of the knee joints, bone tissue and ankle joints. Jelly, mixed meat and edible gelatin should be included in the diet, as these products are natural chondroprotectors that restore cartilage tissue. Complex carbohydrates (vegetables, fruits, whole grain bread), milk protein (cottage cheese, cheese), vitamin and mineral complexes should be on the menu. Food should be steamed or boiled for better digestion.
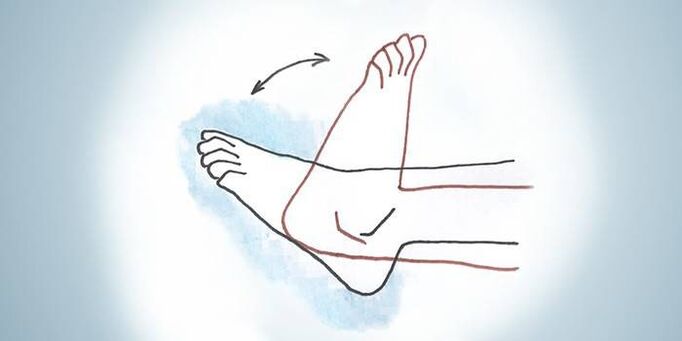
Physical exercises
After the X-ray examination, the doctor can determine the performance of therapeutic exercises. Special exercises for the ankle will help to get rid of pain, relieve muscle tension and restore blood circulation. Examples of exercise therapy exercises:
- sit in a chair, socks and heels take turns to get off the floor;
- the toes stand on the ground, the heel rises, and makes circular motions;
- legs together, feet extending to the side of the body.
Massage
The ankle arthrosis procedure is characterized by a variety of multi-stage techniques. The purpose of the massage is to improve lymphatic and blood circulation in the muscles of the joint cavity, to eliminate poor mobility of the ankle. To relax the muscles, first massage your ankles using kneading and stroking techniques. Then the toes are massaged, then the feet and heels are kneaded. Finish the procedure by working deeply on the ankle joints.

Surgery
If conservative treatment of osteoarthritis does not give a positive result, the attending physician prescribes surgical treatment. It is considered the best among the operating methods:
- Ankle endoprosthesis. An ultra-modern ceramic or metal prosthesis is partially or completely replaced where cartilage is destroyed.
- Ankle arthrodesis. It is prescribed for serious destruction of joint surfaces. During the operation, the bones are rigidly fixed by internal contact.
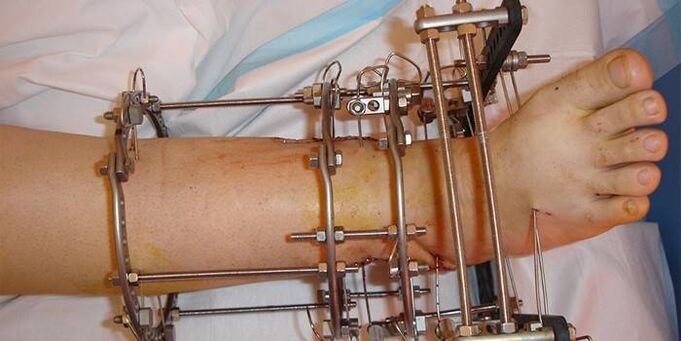
Traditional methods
Village recipes help in the complex treatment of ankle joints for osteoarthritis:
- Chalk and kefir. Mix the two ingredients. Apply this mixture to painful joints at night to reduce swelling.
- Butter and cinquefoil root. Mix the ingredients in a 10: 1 ratio and apply to the injured joint overnight to reduce pain.
Prevention of ankle arthrosis
To reduce the risk of developing ankle osteoarthritis, the following preventive measures should be followed.
- body weight management;
- proper nutrition;
- wear comfortable shoes that do not have high heels;
- avoid joint injuries;
- timely treatment of endocrine and vascular diseases;
- regular performance of gymnastics for the ankle.

Image of ankle arthrosis