Osteoarthritis of the foot is one of the most common types of pathology localized in the articular apparatus of the distal lower extremities.
Adverse effects of destructive joint disease include chronic pain and loss of motor function. Degenerative damage to articular tissues occurs as a complication after regular heavy loads on the foot, after injuries and concomitant diseases. Osteoarthritis is accompanied by pain and deformity of the foot.
Treatment consists of correction with orthopedic insoles and relief of symptoms with medication.
What is this?
Simply put, osteoarthritis of the foot is a severe injury to the joints of the arch of the foot associated with the gradual degeneration and complete destruction of cartilage tissue in them. In addition to the pathological severe pain syndrome, it results in the inability of the foot to function fully, its wear and tear and other functions, and, accordingly, the patient's disability.
Causes
Causes of osteoarthritis of the foot are mainly deterioration of the supporting tissues due to poor blood flow, injuries or age-related changes. For effective treatment, it is necessary to know what causes osteoarthritis of the foot.
The main root causes are described below:
- Excess weight puts more pressure on the joints of the legs.
- Deterioration of bone and cartilage tissue over the years.
- Genetic predisposition.
- Walk in narrow or oversized shoes.
- Individual features of the foot: large width, curvature of the toes, straight legs. In addition, it can cause different leg lengths.
- Excessive mechanical workload of the limbs, which is characteristic of people who prefer heavy physical labor or some sports.
- Traumatic lesions of the legs, muscle spasms.
- Constant cold movement.
- Wear high heels.
In addition, the following causes of osteoarthritis of the foot are distinguished:
- allergies and autoimmune diseases;
- hip dislocation or congenital malformation;
- hormonal and endocrine disorders in the body;
- lack of useful and vital elements;
- chronic infectious lesions of the limbs.
It is not possible to completely cure such a disease, but it is quite possible to significantly improve the patient's quality of life by stopping subsequent degenerative tendencies. In this regard, osteoarthritis of the foot should be treated after identifying the first signs of the disease.
What is the risk of osteoarthritis of the foot?
In the absence of competent and timely treatment, arthrosis of the joints of the foot progresses fairly quickly, leading to the destruction of cartilage tissue and inflammatory processes in the muscles.
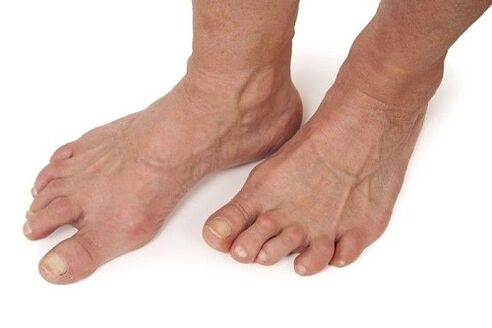
This is accompanied not only by severe pain, but also by deformity of the foot, an increase in bone tissue in the joints. As a result, mobility is lost to such an extent that it is impossible to move the foot. This leads to disability, inability to move independently, as well as psychological distress due to a sense of inferiority.
Symptoms of osteoarthritis of the foot
Osteoarthritis of the foot is accompanied by different severity of symptoms, the degree of manifestation depends on the stage and severity of the lesion. As a rule, the disease begins gradually and may not show external symptoms for a long time.
In addition to fatigue of the feet after a long walk, there are signs of small deformities: the formation of a small bone protrusion in the metatarsophalangeal joint of the big toe, a change in the shape of the toes. A person may perceive these symptoms as an unpleasant cosmetic defect and may be unaware of the existence of a devastating disease.
The main symptoms of osteoarthritis of the foot:
- After waking up, the joints become stiff, they lose mobility, and after a short warm-up, the elasticity returns to the feet;
- In the later stages of the pathology, the range of motion is sharply reduced, the person involuntarily tries to loosen the aching leg, so that gait is impaired and lameness is seen;
- Painful aches as a result of long-term physical exertion, pain syndrome is always present after the joint is completely destroyed;
- Painful aches may appear with changes in the weather or hypothermia of the legs;
- The affected area is periodically swollen, hyperemia with inflammation of the joint, the skin becomes warm to the touch;
- During the movement of the foot, a raspy sound is heard, which is the result of a lack of synovial fluid and bone deformities in the joint;
- Gradually the degenerative process spreads to the periarticular tissues, dense cysts form in the muscles;
- Calluses appear under the feet;
- A person intuitively protects a painful leg, which leads to muscle atrophy and decreased blood circulation;
- Osteoarthritis of the foot is accompanied by rapid fatigue of the legs after standing in one place for a long time or after a short walk.
Lack of therapeutic measures contributes to the development of pathological processes. Continuous changes in the structure of the cartilage and the structure of the joint lead to the appearance of a characteristic clinical picture.
Diagnostics
X-ray technique is crucial in diagnostics. In medicine, the classification of the X-ray stages of osteoarthritis of the foot, proposed in 1961 by a doctor of medical sciences, professor, a leading specialist in the diagnosis of osteoarticular pathologies, is used. It covers three stages:
- Initially, the radiograph shows a slight narrowing of the intervertebral space, which is noticeable only in comparison with a healthy joint, and a weakly expressed damage to the articular cartilage;
- The stage of pronunciation changes - the narrowing of the intervertebral space is clearly visible, because it is two or more times less than normal. The destruction of cartilage tissue takes on an open character where there is the greatest load on the joint;
- Phase of pronunciation changes - X-rays show complete destruction of the cartilage of the bone. There is practically no interarticular space, the bone tissues of the joints are in contact with each other, completely overlap, the surfaces are deformed, bone growths are sharply expressed. This stage is called osteoarthritis of the foot, in which the motor functions of the joints of the foot are severely impaired.
This technique is still used when a person undergoes a medical and social examination to create a disability group. According to Kellgren Lawrence, proposed in 1957, there is another radiological classification of osteoarthritis.
In addition to X-ray, modern methods of instrumental diagnosis of osteoarthritis of the foot are used. Ultrasound examination of the joints of the foot and computed tomography provide additional information about the condition of the bone, cartilage and periarticular tissue in the affected area.
Treatment of osteoarthritis of the foot
It should be noted immediately that therapy should be carried out only in consultation with a physician. Improper treatment of osteoarthritis of the foot at home, performed by some careless patients, only aggravates the disease and delays recovery.
A number of procedures are used to treat osteoarthritis of the feet, including conservative and surgical methods. Conservative methods include:
- Drug treatment - painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs in tablet form, topical and injectable form, chondroprotectants are injected together;
- Physiotherapy - ultraviolet radiation, treatment with high-frequency currents, shock wave therapy, therapeutic exercises and massage, mud applications, mineral baths;
- Spa treatment.
A special problem is the treatment of osteoarthritis of the small joints of the foot. With osteoarthritis of the foot, deformity and curvature of the toes develop very quickly, impeding walking and contributing to the appearance of painful corns and calluses. To prevent such curves, experts recommend changing shoes to more comfortable ones, as well as contacting an orthopedist who will help you choose orthopedic inserts and special tires that keep your toes in the right position.
In the third stage of deforming osteoarthritis of the foot, it is too late to take pills and apply physiotherapy, because at this stage, drug treatment of osteoarthritis of the foot can no longer give a lasting positive result. First, the cartilage membrane is completely destroyed, and then the joint bone tissue. Also, one of the consequences of osteoarthritis of the foot are pathologies of the spine (curvature, herniated intervertebral discs) due to persistent impairment of posture and gait.
Surgical treatment is used to restore normal motor function of the joint. This may include the removal of cartilage debris, the artificial closure of a joint to prevent further bone destruction, and the partial replacement of joint tissue with an artificial one. The radical method of treatment involves a complete replacement of the joint with an endoprosthesis. But all these manipulations are carried out only with one great combination - the ankle.
Lifestyle change
The patient should reconsider a number of habits in daily life that contribute to and stimulate the development of osteoarthritis of the foot. Without it, drug treatment will not have the desired effect. Painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs will not only eliminate the symptoms of the disease, but the pathological process itself will progress.
The first important point when changing your lifestyle is to reduce the stress on the diseased joint. In order to prevent the development of the disease and stabilize the process, it is first necessary to reduce the joint load. This can be achieved by changing certain habits and lifestyle.
The most important rules to reduce the load on the feet are:
- avoid long walks;
- Alternative walk with 5 minutes rest;
- do not stand still for a long time (static load on the affected joint is worse tolerated than dynamic);
- frequent descents and ascents are not recommended, you should use the elevator more often if possible;
- do not carry weight;
- use a cane.
Another important point is to lose weight. As mentioned above, in obese patients, osteoarthritis of the foot progresses faster because of more stress on the joints during walking. For treatment, it is important to determine the so-called body mass index (BMI) and try to normalize this indicator.
Drug treatment of osteoarthritis of the foot
Medications to treat osteoarthritis of the foot at home are reduced to taking certain medications. They partially eliminate the symptoms of the disease, help to improve the nutrition of the joint. The problem is that cartilage and bone deformities are very difficult to repair. Often, surgery is still required for a complete correction. But the tactics of treatment depend on the stage. Before joint changes, the main method is precisely drug treatment.
Prescribing drugs can lead to the development of gastropathy, manifested by erosions and ulcers of the stomach and duodenum. Risk factors for the development of complications are old age, history of gastric ulcer and chronic gastritis, concomitant use of 2-3 drugs from this group.
In order to prevent aggravation, the following is prescribed in parallel:
- Proton pump inhibitors.
- H2 histamine receptor blockers.
Chondroprotectors are used to improve joint function. These are drugs that improve the metabolism of articular cartilage, slow it down and prevent its destruction. The main components of such drugs are glycosaminoglycans and sodium chondroitin sulfate. All chondroprotectors are used for long courses - from 1 to six months. Treatment should be repeated after a break of 2-3 months.
In addition to systemic (whole body) tablets, capsules and injections, topical therapy is also used. This applies to the use of ointments and creams. In addition, some medications are injected directly into or near the ankle. This treatment usually gives a faster and more stable effect.
The following methods can be used for local therapy:
- intraarticular and periarticular administration of glucocorticoids;
- intraarticular application of hyaluronic acid preparations;
- topical application of ointments (gels, creams) based on non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs to the affected joint area.
Physiotherapy
The following physiotherapeutic procedures are used in the treatment of patients with osteoarthritis of the legs:
- Pulse magnetotherapy - inductors are placed on both sides of the affected joint and move slowly for 5-10 minutes. The course consists of 10 procedures.
- Application of heat-transfer fluids - during such procedures the temperature of the affected tissues rises. Cartilage metabolism is activated, its regeneration is stimulated. Peat mud is applied at temperatures up to 40 degrees, paraffin and ozokerite at temperatures up to 55 degrees. Such procedures are performed every 10 to 15 days for a 20-minute course.
- Electrophoresis - lidocaine, analgin, sodium salicylate. Exposure time is 20 minutes a day. The course consists of 15 procedures.
- Ultrafonophoresis - hydrocortisone, analgin. Duration 5 minutes for each affected joint. The course of treatment consists of 10 procedures.
- Infrared radiation - lasts 5 - 8 minutes every day for 10 days in a painful joint.
Gymnastics
In the acute period of osteoarthritis of the legs of the lower extremities, the legs are shown to be at rest. However, as soon as the pain subsides, you need to start exercise therapy.
Exercises that can be done at home for osteoarthritis of the legs:
- take turns taking the socks away from you and pulling them towards you;
- make circular motions with your thumb;
- squeeze the toes as tightly as possible and also open them vigorously;
- try to pick up small objects from the ground with your toes.
If the patient has osteoarthritis of the small joints of the foot, exercise therapy (kinesitherapy) is considered essential. It is better to learn with an instructor first - he will show you what and how to do it
Wear special shoes
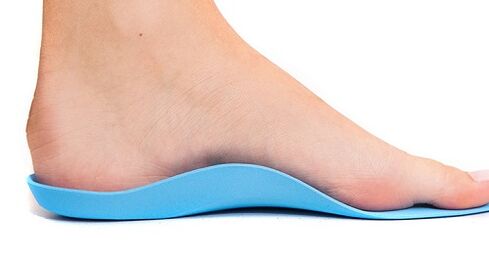
With the complex treatment of osteoarthritis of the foot, doctors prescribe regular wearing of special shoes. It is now easy to find orthopedic boots, shoes and even shoes for home use on sale.
Specially designed footrests and soles support the foot in the desired position and increase the ability to absorb impact while walking, while brackets and attachments straighten the ankle, preventing further deformation of articular cartilage and the development of arthrosis of the toes.
Folk remedies
The following folk remedies are most effective for the treatment and prevention of osteoarthritis:
- Potato compresses. They are mainly used to relieve swelling and pain in the affected joint area. Potatoes are thoroughly washed and cut without peeling. Then throw in warm water (40-50 degrees) and soak for a few minutes. The resulting mass is wrapped in cloth and applied to the affected joint twice a day.
- Angelica root baths. Angelica root is crushed and wrapped in a cloth (the gauze is folded several times). For 5 liters of water you need 250 - 300 g of carrots. The piece is placed in a bowl with boiling water and wait for the water to cool to a temperature of 30-40 degrees. After that, foot baths are done for 10-15 minutes. In this case, the bag is not removed.
- Poppy oil. Twice a day, poppy oil is applied to the affected joint area. For best effect, it is recommended to apply a warming compress before applying the ointment.
- Garlic juice. A few cloves of young garlic are ground until juicy and vegetable oil is added. The resulting mixture is applied to the painful joint with a thin layer before going to bed and apply a bandage.
- Coniferous balm. This tool helps to improve metabolism in cartilage tissue, delays the deformation of the joint. To prepare the balm, 50 g of young needles are poured into 2 liters of boiling water. Boil the mixture on low heat for 15-20 minutes. At this time you can add a teaspoon of garlic juice, hips puree, finely chopped licorice root. The broth is brewed in a thermos for 18-20 hours. After that, it is filtered through gauze, cooled in the refrigerator and drunk 0. 5 - 1 liter per day for a week.
- Ointment from hops and St. John's wort. To prepare the ointment, finely chop 10 grams of washed St. John's wort and hops. Add 50 g of Vaseline oil to the resulting solution and mix well until a homogeneous mass is obtained. The ointment is applied to the joint area twice a day.
The above remedies are recommended for people at risk of developing osteoarthritis of the feet. First of all, these are patients suffering from rheumatoid arthritis and other inflammatory diseases of the joints. As a prophylactic measure, these prescriptions can also be used by the elderly, athletes, and patients after ankle fractures or sprains.
Surgery
Osteoarthritis of the foot is a chronic pathology in which degenerative processes gradually progress and worsen. In stage 3 of the disease, the disorders become so obvious that the cartilage tissue is completely destroyed and cannot be repaired with drugs. Only surgical methods are used to remove the deformity, severe pain, and restore the ability to walk. The remaining treatments are ineffective.
Types of modern surgical interventions:
- Arthroscopy. An arthroscope is inserted into the intraarticular space - a special device that allows you to examine the joint from the inside. The doctor removes all foreign elements from the synovial fluid: broken cartilage particles, bones or blood clots. Manipulation reduces the severity of pain, but provides temporary relief. The pain returns within 6-12 months. Mainly used in young people;
- Arthrodesis. During the operation, the remaining cartilage is removed, the joint is fixed in one position. Gradually, the bones come together in a certain position, so ankylosis appears. The joint is completely removed, which leads to immobility of the foot, but the removal of pain, inflammation and the ability to walk, although the quality of movement still remains low. The technique is rarely used;
- Endoprostheses. It is used only in stage 3 of the disease, when there is practically no cartilage left. The method consists of implantation of an implant. Depending on the type of material used, the service life is 10-15 years. Endoprostheses allow you to completely restore your quality of life.
Is it possible to completely cure osteoarthritis of the foot?
It is believed that it is impossible to completely cope with osteoarthritis of the foot. Destroyed cartilage no longer grows. All therapy is aimed at maintaining the current condition of the joint and keeping the patient in the form in which he came to the doctor.
The doctor can only stop the process, but not restore the tissue. If the recommendations are followed, the patient will not feel restricted in movement, and only negative external factors or disregard for the doctor's advice may again cause discomfort in a person's legs.
Prevention and complications
You need to follow simple rules to rule out the appearance of an unpleasant disease. One of them is a healthy lifestyle. To prevent osteoarthritis, you need:
- reduce the amount of salt you eat;
- to organize proper nutrition;
- limit excessive physical activity;
- get rid of excess weight;
- Strengthen immunity to exclude inflammatory, infectious diseases.
Preventive measures for the development of osteoarthritis include:
- to prevent damage to the lower extremities;
- exclusion of hypothermia of the legs;
- self-massage of the sole;
- use of comfortable shoes with elastic soles, orthopedic insoles;
- removal of high heels;
- perform gymnastics for the joints of the foot;
- walking barefoot on grass and sand;
- timely treatment of inflammatory diseases.
The disease can be complicated by pathologies such as arthritis, leg bursitis, inflammation of the periarticular bursa. Osteoarthritis of the foot leads to deformity of the toes, which in a careless position causes immobility of the foot and disability of the patient.
Forecast
Prognosis is favorable with timely diagnosis of osteoarthritis of the foot and properly selected treatment in the early stages. Although the destruction of cartilage is irreversible, the destruction of the joint can prevent further progression of the pathology. In the later stages, osteoarthritis has an unfavorable prognosis, the function of the foot is lost, and the prevention of disability can only be replaced by an artificial joint.



































